Top 10 Allergic Bronchitis Symptoms You Should Know for Better Health
Allergic bronchitis occurs when allergens irritate the bronchial tubes, causing inflammation, mucus production, and difficulty breathing. Is allergic bronchitis dangerous for those who experience frequent symptoms like coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath?
This condition can lead to ongoing respiratory issues, especially in individuals with pre-existing lung problems. It’s understandable to feel concerned about chronic symptoms; however, with proper care, doctors can effectively manage the condition.
In this blog, we will evaluate the allergic bronchitis symptoms and offer practical advice for managing the condition to improve your lung health.
Key Takeaways:
- Allergic bronchitis symptoms include persistent cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
- Avoiding allergens, using prescribed medications, and managing indoor air quality are key to controlling symptoms and preventing flare-ups.
- Early diagnosis and treatment by a bronchitis specialist can help manage symptoms effectively and improve long-term lung health.

What Is Allergic Bronchitis?
Allergic bronchitis occurs when allergens, such as dust or pollen, trigger an immune response in the bronchial tubes. It results in inflammation and excess mucus, making breathing difficult. It differs from acute bronchitis in that it persists over weeks or months and usually stems from allergic triggers or pollution rather than infection.
Moreover, chronic bronchitis, which is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), accompanied by emphysema, also lasts for months or longer.
Let’s look at some of the symptoms of allergic bronchitis you must know.
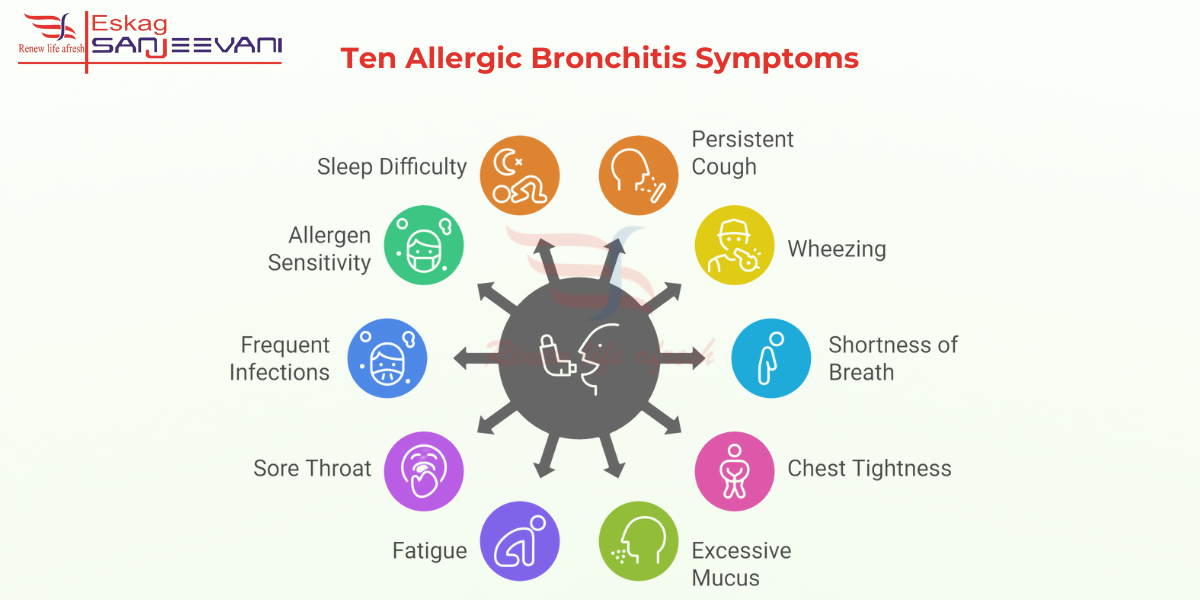
10 Key Allergic Bronchitis Symptoms
Allergic bronchitis symptoms occur when allergens trigger inflammation in the bronchial tubes, causing discomfort and breathing difficulties. These symptoms can range from mild irritation to severe respiratory issues, affecting everyday life.
Here are ten allergic bronchitis symptoms which affect lung health:
1. Persistent Cough
A chronic, non-productive cough is a hallmark of allergic bronchitis, typically worsening at night or during exposure to allergens. The cough is often dry but can sometimes produce mucus. This symptom can be mistaken for a cold or infection, but lasts longer than usual respiratory illnesses.
2. Wheezing
Wheezing is often a characteristic symptom of allergic bronchitis, and a whistling sound is frequently heard during breathing. It results from airway obstruction caused by mucus production and rapid inflammation. The characteristic wheezing sound is a clear indication of nasal obstruction and requires medical intervention.
3. Shortness of Breath
Individuals with allergic bronchitis may experience shortness of breath, especially with physical activity or when exposed to allergens. Such inflammation can make breathing difficult, causing chest tightness. This symptom indicates that the respiratory system is under stress.
4. Chest Tightness
Individuals with allergic bronchitis often report chest tightness and can feel like pressure or constriction in the chest. This symptom is associated with airway inflammation and can worsen when the person is exposed to allergens or pollutants. It can make breathing seem more laborious.
5. Excessive Mucus Production
The body produces excess mucus to trap and clear allergens from the airways. It leads to frequent throat clearing and coughing to expel the mucus. In some cases, mucus can accumulate in the lungs, leading to further discomfort.
6. Fatigue
Fatigue is a common complaint for individuals with allergic bronchitis due to the body’s ongoing effort to combat inflammation. Disrupted sleep from coughing or wheezing at night can also contribute to feeling constantly tired. Fatigue can affect daily activities and quality of life.
7. Sore Throat
A persistent sore throat may develop from chronic coughing or from allergen-induced irritation. The throat becomes dry and scratchy from the effort of coughing and mucus production. This symptom can also occur if the mucus drains down the back of the throat, irritating it.
8. Frequent Respiratory Infections
People with allergic bronchitis are more prone to upper respiratory infections because the inflammation weakens the respiratory system’s ability to fend off germs. These infections lead to additional symptoms, such as fever or more intense coughing. Recurring infections may indicate poorly controlled allergic bronchitis.
9. Increased Sensitivity to Allergens
Those with allergic bronchitis may become more sensitive to airborne allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander. Exposure to these allergens can immediately worsen symptoms like coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Managing allergen exposure is crucial to preventing flare-ups.
10. Difficulty Sleeping
Allergic bronchitis symptoms, such as coughing and wheezing, can severely disrupt sleep. With persistent airway inflammation and mucus accumulation, individuals have difficulty breathing. Moreover, such poor-quality sleep leads to increased fatigue and a general decline in quality of life.
Next, let’s explore some of the prominent risk factors and triggers for allergic bronchitis.
Common Triggers of Allergic Bronchitis
Long-term exposure to pollen, dust and other allergens is one of the primary causes for allergic bronchitis. A study shows that 26% of individuals link their symptoms to dust exposure 1.
Here are some of the common triggers for allergic bronchitis:
- Exposure to dust and allergens triggers the production of histamines, leading to inflammation of the bronchial tubes.
- Moreover, exposure to other airborne irritants leads to chronic bronchitis, especially with exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Individuals who are over 40 years old are susceptible to allergic bronchitis and, therefore, are a critical risk factor for the condition.
- A genetic condition is also a significant trigger, where individuals with a deficiency of alpha-1-antitrypsin and a family history of COPD also experience allergic bronchitis.
With a better understanding of the common triggers and risk factors, let’s explore how to diagnose allergic bronchitis.
How Allergic Bronchitis Is Diagnosed
Diagnosing allergic bronchitis involves evaluating symptoms and identifying potential allergens that trigger bronchial inflammation. Doctors assess medical history, conduct physical examination, and perform specific tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Here are some of the effective management strategies for allergic bronchitis:
- Medical History: The doctor reviews your symptoms, their duration, and potential allergen exposure to distinguish allergic bronchitis from other conditions.
- Physical Examination: The doctor listens to your lungs for signs of wheezing or inflammation, which helps assess airway obstruction.
- Pulmonary Function Tests: Spirometry measures lung function to check for airflow obstruction and assess the severity of bronchial inflammation.
- Allergy Testing: Tests for skin and blood help in isolating potential allergens which cause bronchitis and guide doctors in creating treatment plans.
- Chest Imaging: A chest X-ray or CT scan may be used to rule out other lung conditions or structural abnormalities.
Exhaled Nitric Oxide Test: This test measures airway inflammation, providing further evidence of allergic bronchitis.
Also read: All You Need To Know About Winter Lung Care.
Effective Management of Allergic Bronchitis
A review of clinical studies found that use of HEPA‑based air filtration in homes reduced indoor particulate matter (PM) by 30% to 70% 2.
Here are some of the allergic bronchitis treatments for early assessment of the condition:
- Minimising contact with allergens like dust, pollen, and pet dander is essential. Regular cleaning, using dust‑mite covers, and reducing exposure to smoke can help reduce flare-ups.
- Air purifiers with HEPA filters reduce airborne allergens and fine particles, helping reduce airway inflammation and improve breathing.
- Medications such as antihistamines, inhaled steroids, or bronchodilators can help manage inflammation and mucus production. Consult with a doctor for tailored treatment.
- Keeping indoor humidity levels in check, ensuring proper ventilation, and avoiding smoking or exposure to polluted air can reduce lung strain and help maintain overall respiratory health.
Why Choose Eskag Sanjeevani for Chest Care?
To effectively manage allergic bronchitis symptoms, avoid allergens, maintain a clean environment, and follow treatments. At Eskag Sanjeevani Hospitals, we offer expert care from the best pulmonologist in Kolkata, ensuring effective diagnosis and management.
Our team provides personalised treatment plans tailored to your specific needs, improving long-term lung health. If you experience symptoms, seeking consultation with a bronchitis specialist can prevent further complications.
Eskag Sanjeevani’s specialists work closely to isolate risk factors and optimise your treatment.
References
Treatment for allergic bronchitis typically involves avoiding allergens, using antihistamines, and inhaled steroids to reduce inflammation. Bronchodilators may also be prescribed to help open airways and ease breathing.
Rest, staying hydrated, and using prescribed medications, such as corticosteroids or bronchodilators, can help speed recovery from bronchitis. Avoiding irritants and managing symptoms with over-the-counter cough suppressants may provide relief.
An allergic cough is often dry and occurs due to long-term exposure to allergens such as dust. Additional symptoms include itchy eyes and a runny nose.
Yes, allergies can cause wheezing when allergens trigger inflammation and narrowing of the airways, making breathing harder. It is common in individuals with allergic asthma or allergic bronchitis.
Upper respiratory allergies typically cause symptoms like sneezing, a runny or stuffy nose, itchy eyes, and post-nasal drip. These symptoms often occur in response to allergens like pollen, dust mites, or pet dander.

