The Link Between COPD and Heart Disease: What You Should Know
COPD and heart disease often occur together, placing a heavier burden on your overall health and treatment needs. In India, the prevalence of COPD among adults is about 7.4 % 1.
You may feel anxious or unsure when symptoms overlap, but understanding the connection can help you take confident steps toward better care. It matters that you recognise how both conditions interact so that you can make informed choices for your health.
In this blog, we will evaluate the link between COPD and heart disease and what you need to know to protect yourself from such illnesses.
Key Takeaways:
- COPD and heart disease often coexist, increasing the risk of complications and requiring a tailored treatment approach for both conditions.
- Shared risk factors like smoking, inflammation, and air pollution contribute to the development of both COPD and heart disease.
- Managing both conditions involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups to control symptoms and improve quality of life.
- The Link Between COPD and Heart Disease: What You Need to Know
- Shared Risk Factors: How COPD and Heart Disease Are Connected
- Managing COPD and Heart Disease: Key Treatment Approaches
- How Lifestyle Changes Can Improve COPD and Heart Health
- Recognising Symptoms: When COPD and Heart Disease Occur Together
The Link Between COPD and Heart Disease: What You Need to Know
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and heart disease often coexist, with studies showing that people with COPD have a greater risk of developing cardiovascular conditions. The link arises with the effects of shared risks such as smoking, inflammation, and poor lung function.
- Inflammation: Both COPD and heart disease involve chronic inflammation that affects the blood vessels and the lungs. Persistent inflammation can narrow blood vessels, increasing the risk of a heart attack.
- Poor oxygen levels: COPD reduces the overall oxygen concentration in the blood, straining your heart, particularly the right side. Such a condition leads to severe cardiovascular issues and heart failure.
- Atherosclerosis: Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are at increased risk of atherosclerosis, in which arteries narrow due to plaque buildup.
- Smoking: Smoking is a leading cause of both COPD and heart disease. There is severe damage to blood vessels, reduced lung function, and pulmonary infections. Therefore, smoking cessation is necessary for the prevention of COPD and heart disease.
Now, let’s examine some shared risk factors for COPD and heart disease.
Shared Risk Factors: How COPD and Heart Disease Are Connected
Recent studies show that nearly 27% of COPD patients in India also experience co-existing cardiovascular issues, particularly coronary artery disease 2.
Several shared risk factors influence the connection between COPD and heart disease:
- Chronic inflammation: Both COPD and heart disease are driven by chronic inflammation. The long-term airway inflammation in COPD contributes to systemic inflammation, which can also damage the heart and blood vessels over time.
- Air pollution exposure: Living in areas with high air pollution enhances the risk of both COPD and heart disease. Pollutants such as particulate matter can irritate the lungs and accelerate the development of arterial plaque, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Age and metabolic conditions: Older adults, particularly those with obesity or high blood pressure, are at higher risk for both COPD and heart disease. These conditions contribute to the deterioration of lung and heart health by causing strain on both systems.
- Sedentary lifestyle: A lifestyle which is sedentary lifestyle contributes to the development of both COPD and heart disease. Physical inactivity can worsen lung function and increase the likelihood of obesity and poor cardiovascular health.
Let’s now understand how you can manage COPD and heart disease to prevent heart disease.
Managing COPD and Heart Disease: Key Treatment Approaches
The management of both COPD and heart disease requires a multifaceted approach due to the complex interplay between the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
- Pharmacological management: Medications such as long-acting bronchodilators for COPD and antiplatelet agents or beta-blockers for heart disease should be carefully coordinated to avoid interactions.
- Oxygen therapy and ventilatory support: Patients with severe COPD or lung disease may use LTOT (long-term oxygen therapy) to maintain a stable oxygen concentration. Moreover, the strategy helps reduce strains on the right side of the heart.
- Exercise and physical rehabilitation: Pulmonary rehabilitation, which includes tailored exercise programmes, improves both lung capacity and cardiovascular endurance.
- Comorbidity management: Cardiovascular risk factors such as diabetes and elevated blood pressure are critical for managing both COPD and heart disease.
- Monitoring and early intervention: Regular follow-up with spirometry, echocardiography, and other diagnostic tools is essential for early detection of exacerbations or disease progression.
With a better understanding of heart disease prevention, let’s explore some lifestyle modifications you can make for a sustained life.
How Lifestyle Changes Can Improve COPD and Heart Health
Lifestyle changes are essential for the management of COPD and heart disease, as they address shared risk factors and improve overall health.
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking halts the progression of COPD and reduces cardiovascular risk by eliminating inflammation and improving lung function.
- Regular exercise: Exercise improves overall cardiovascular health and lung capacity. It also reduces breathlessness among COPD patients.
- Balanced diet: Intake of fruits and vegetables helps blood pressure, cholesterol, and inflammation, benefiting both the heart and lungs.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight eases strain on the heart and lungs, improving overall function and reducing the risk of complications.
- Stress management: Reducing stress through mindfulness and relaxation techniques can lower inflammation, improving both respiratory and heart health.
Also read: Pulmonary Fibrosis: Early Signs, Causes, and Treatments
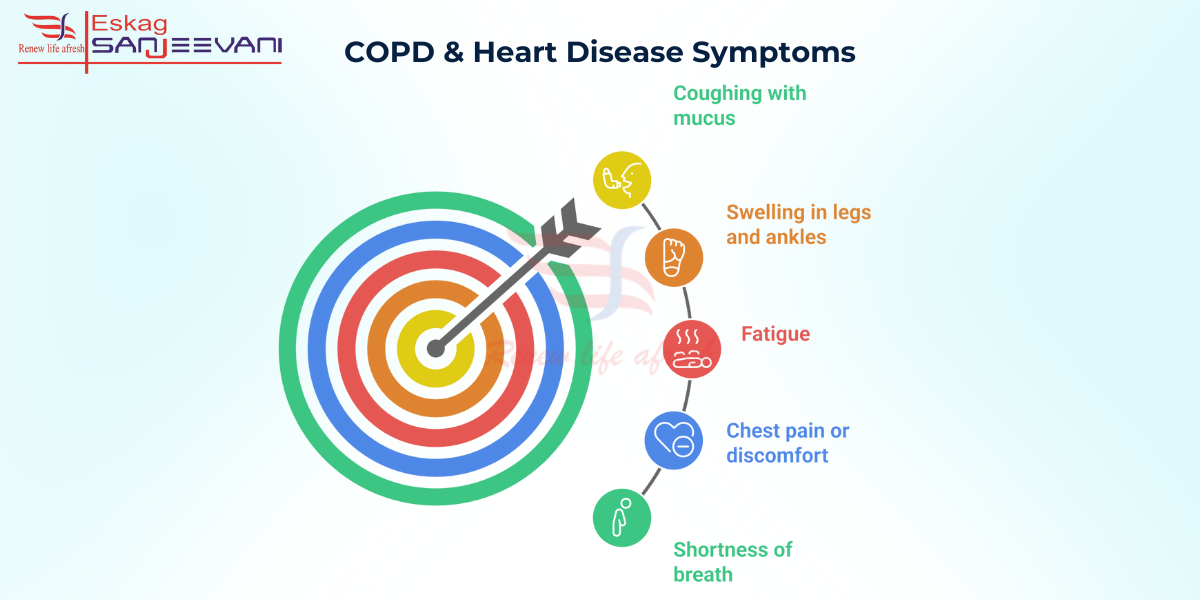
Recognising Symptoms: When COPD and Heart Disease Occur Together
When COPD and heart disease occur together, the overall symptoms overlap, which requires complex diagnosis and treatment.
- Shortness of breath: Severe breathlessness during minimal activity may indicate both heart failure and COPD, requiring urgent evaluation.
- Chest pain or discomfort: Persistent chest pain, especially with exertion or swelling, may signal both heart disease and COPD.
- Fatigue: Chronic, unexplained fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest can be a sign of both conditions worsening.
- Swelling in legs and ankles: Fluid retention due to heart failure combined with COPD can cause swelling in the lower extremities.
- Coughing with mucus: Increased mucus production or blood in the cough suggests worsening COPD or a cardiovascular issue and requires medical attention.
If you are looking for early diagnosis of symptoms, Eskag Sanjeevani Hospitals offer the best pulmonologists and expert guidance on managing COPD and heart disease.
Final Thoughts
Management of COPD and heart disease cohesively requires a multifaceted approach, as both conditions have risk factors. It’s critical to understand both respiratory and cardiovascular health, and to prioritise each factor for a better lifestyle.
At Eskag Sanjeevani Hospitals, we provide comprehensive care for patients with COPD, with a team of specialists focused on both conditions. If you are looking for effective treatment for COPD patients, we can provide tailored approaches for better health outcomes.
References
Yes, COPD can affect the heart due to chronic inflammation and reduced oxygen levels, which strain the cardiovascular system. It can lead to heart enlargement, particularly the right side of the heart, and eventually heart failure.
COPD primarily affects the right side of the heart, leading to right-sided heart failure or cor pulmonale. It occurs because increased pressure in the pulmonary arteries results from poor lung function.
Severe COPD can lead to cor pulmonale, where the right side of the heart enlarges and weakens due to increased pulmonary pressure. It can cause symptoms like swelling, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
Yes, COPD can lead to heart problems by causing high blood pressure in the lungs and increasing the risk of heart failure. Chronic inflammation from COPD contributes to plaque buildup in the arteries, further damaging heart health.
Treatment for COPD in heart failure involves managing both conditions with medications to control symptoms and improve heart function. Oxygen therapy and diuretics may be used to reduce fluid retention and improve breathing.

