What Is Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Guide to Managing Crohn’s and Colitis
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of small intestine and colon inflammatory conditions which often lead to severe complications in the gut. In 2019, the total number of IBD cases in India was 270,719 and for many, there are several challenges associated with symptoms of physical health. Understanding the complexities of what is inflammatory bowel disease can help you make informed decisions and improve your lifestyle.
In this blog, we will explore what is IBD, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options to manage the condition.
- What is IBD?
- Different Types of IBD: Explore Differences Between Crohn’s & Ulcerative Colitis
- Causes & Risk Factors for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
- Common Symptoms of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
- How to Diagnose IBD: Tests You Must Know About?
- Treatment Strategies for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
- Futures Aspects for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
- Take Control of Your Gut Health
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) generally include two main conditions, namely Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative Colitis (UC). Both conditions cause severe inflammation of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Despite shared similarities between the two conditions, there are differences which are critical to understand what is inflammatory bowel disease.
To summarise, there are healthy sections of the intestines mixed in between the inflamed areas in the case of Crohn’s disease. However, in the case of ulcerative colitis, there is a continuous inflammation of the colon.
Let’s now understand the causes to understand what inflammatory bowel disease is and its risk factors.
Different Types of IBD: Explore Differences Between Crohn’s & Ulcerative Colitis
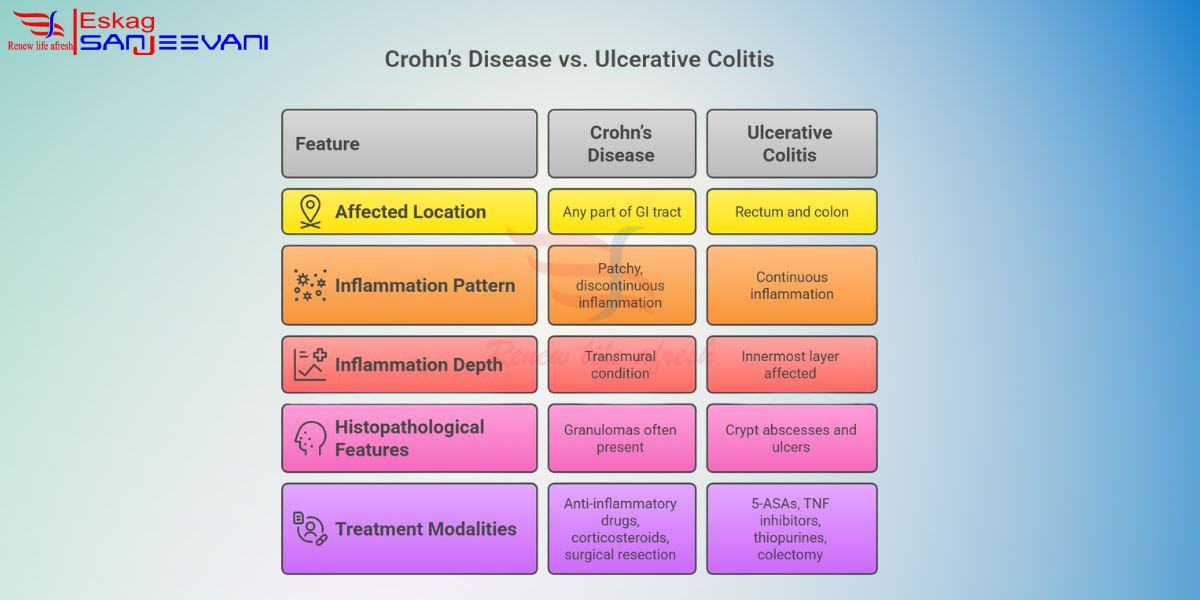
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) generally include two main conditions, namely Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative Colitis (UC). Both conditions cause severe inflammation of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Despite shared similarities between the two conditions, there are differences which are critical to understand what is inflammatory bowel disease.
Crohn’s Disease:
- Affected location: It can affect any part of the GI tract. It includes the oesophagus, small intestine, and colon.
- Inflammation Pattern: The pattern resembles a patchy and discontinuous inflammation with the presence of healthy tissue between the affected areas.
- Inflammation Depth: The condition affects all the adjacent layers of the bowel wall, which is also known as a transmural condition.
Histopathological features: Granulomas are often present in biopsy samples. - Treatment modalities: Anti-inflammatory drugs (5-ASAs), corticosteroids, and surgical resection are used in severe conditions.
Ulcerative Colitis (UC)
- Affected location: UC is predominantly confined within the rectum and colon.
- Inflammation Pattern: There is a continuous inflammation, which typically starts from the rectum and extends to the proximal region in a contagious manner.
- Inflammation Depth: Affects the innermost layer of the bowel wall.
- Histopathological features: Inflammatory infiltration of the mucosa with crypt abscesses and ulcers.
- Treatment modalities: 5-ASAs (mesalamine), TNF inhibitors, thiopurines (immunosuppressants), and colectomy in refractory cases.
To summarise, there are healthy sections of the intestines mixed in between the inflamed areas in the case of Crohn’s disease. However, in the case of ulcerative colitis, there is a continuous inflammation of the colon.
Causes & Risk Factors for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
There is no single risk factor associated with IBD; however, there is a combination of factors which lead to chronic inflammation and further complications.
Here are some of the prominent risk factors for IBD:
- Genetics and Family History: The Presence of a parent or sibling in a family is one of the strongest known risk factors for developing IBD. Such risk is significantly higher than that of the general population. Studies suggest that approximately 20% of people affected with IBD have a relative suffering from the condition.
- Environmental Risks: Overall disruptions in the gut microbiota, which is also known as dysbiosis, are one of the primary factors in IBD. Some of the early life factors include antibiotic use in infancy. Moreover, environmental pollutants such as industrial chemicals and microplastics are also linked with higher risks of IBD.
- Lifestyle Factors: Some of the lifestyle factors include excessive smoking, with the overuse of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, which can cause irritation in the gut and negative and worsen the condition of the IBD.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Increased engagement in a sedentary lifestyle is associated with IBD risks, and regular exercise is an easy way to affect such conditions.
- Use of Oral Contraceptives: Certain studies suggest that continuous use of hormonal therapies and oral contraceptives can pose a prominent risk factor for IBD. Women using oral contraceptives may have a slightly higher chance of developing Crohn’s disease.Now let’s understand what the signs and symptoms are to understand what IBD is and how to tackle it at the early stages.
Common Symptoms of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
The symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can significantly affect daily lives, with individuals suffering from excruciating pain and systemic digestive issues. Understanding what is inflammatory bowel disease is essential to recognising its symptoms, which in most cases involve abdominal pain, chronic diarrhoea, fatigue, and unintended weight loss.
Here are some of the common symptoms that you must know:
- Abdominal pain and cramping: Persistent pain and discomfort, which is often linked with inflammation in the bowel. Patients suffering from such a condition often feel pain in the lower abdomen; however can vary based on different areas.
- Fatigue: It is a common symptom of IBD, and in most cases, it leads to chronic conditions. Fatigue is also caused due to malabsorption of nutrients and inflammation.
- Loss of weight: It is a common symptom of Crohn’s disease, and you may experience unexpected weight loss. Moreover, loss of weight is also accompanied by inflammation in the small intestine, which disrupts the overall disruption of the GI tract.
- Presence of blood in stool: It is a common symptom of Ulcerative Colitis and usually occurs when the colon is affected. There can be signs of dark red blood, which depends on the extent of haemorrhage.
- Other symptoms: There are subsidiary symptoms other than digestive symptoms, such as fever, joint pain, and skin conditions. Moreover, IBD also increases the risk of iron deficiency anaemia in women.
For accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of IBD, consulting with the best gastroenterologist in Kolkata provides access to expert care and personalised treatment options.
How to Diagnose IBD: Tests You Must Know About
- Diagnosis of IBD involves a combination of clinical evaluation. Laboratory tests, endoscopic procedures, and imaging studies are used to determine the extent of inflammation. Understanding what is inflammatory bowel disease helps clinicians select diagnostic tools that differentiate it from other gastrointestinal disorders.Here’s how you can diagnose IBD:
- Physical examination: Doctors may examine the abdomen with gentle pressing to check for any pain or tenderness. Other signs include eye inflammation, skin rashes, and irritation.
- Blood Test: Blood tests can help reveal signs, which include markers that are responsible for indicating inflammation and anaemia. Lower levels of iron, folate, vitamin D, and vitamin B12 indicate nutritional deficiency, which indicates nutrient malabsorption.
- Stool Test: It is an important diagnostic test that measures the severity of inflammation and the presence of blood, which may not be visible to the naked eye.
- Endoscopic Procedures: Colonoscopy is used to diagnose Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis in the form of video images to investigate the intestinal lining for signs of ulcers and other signs of inflammation.Also read: Eskag Sanjeevani Hospital’s Comprehensive Health Check-Up Packages: What’s Included & Why It MattersNow, let’s explore some of the prominent treatment strategies which can help you understand how to cure inflammatory bowel disease with ease.
Treatment Strategies for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
The treatment procedures for inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) aim to decrease inflammation and induce long-term remission. Exploring what is inflammatory bowel disease and its treatment is critical when it comes to isolating what is the best medicine for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.Here is a comprehensive insight into different treatment strategies to tackle IBD:
- Medication: Aminosalicylates, for example, mesalamine, help reduce the inflammation in the intestinal lining and are used to treat ulcerative colitis. Corticosteroids are popular for reducing inflammation during flare-ups of IBD. Moreover, anti-TNF agents such as infliximab and adalimumab target specific molecules to treat severe cases of IBD.
- Nutritional Therapy: Nutritional therapies involve the use of specialised liquid formulas and dietary alterations, which help in stabilising the intestinal lining. Moreover, in severe cases of IBD, total parental nutrition (TPN) is a potent therapy to improve the overall healing process.
Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding spicy foods or foods with high fibre can help avoid the signs and symptoms of IBD. Stress reduction techniques such as meditation and yoga can help you manage the negative implications of IBD.Also read: Why Eskag Sanjeevani is Among the Best Hospitals for Gastroenterology in Kolkata?Futures Aspects for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
The future of managing inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) looks promising with ongoing advancements in therapeutic approaches. Understanding what is inflammatory bowel disease is continues to guide scientific exploration aimed at improving patient outcomes, achieving long-term remission.
Here are some of the key aspects shaping IBD treatment:
- Personalised Medicine: Precision-based treatment models are being developed through proteomic and microbiome profiling. These approaches help predict how patients respond to a specific therapeutic strategy.
- Microbiome-Targeted Therapies: Gut microbiota have a critical role in maintaining intestinal balance, and such therapies include microbiota restoration techniques such as faecal microbiota transplantation (FMT).
- Next-Generation Biologics: Biological drugs such as interleukin (IL)-23 inhibitors and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors offer higher efficiency and fewer side effects compared to traditional immunosuppressants.
- Stem cell therapy: Mesenchymal stem cell therapy helps repair damaged intestinal tissues and improve immunological response, and provides better resistance compared to conventional treatments.
Take Control of Your Gut Health
Managing inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) requires consistent medical attention to understand how the condition affects the gastrointestinal system. Understanding what inflammatory bowel disease is helps you isolate potential triggers, reducing flare-ups and enhancing long-term health outcomes.
Negative health effects, such as fatigue and abdominal pain, affect daily operations. Following a gut-friendly diet and following medical advice from your physician can help you improve the quality of your life.
Eskag Sanjeevani hospital is one of the best hospitals in Kolkata, which provide expert gastroenterology care with advanced diagnostic support for patients with inflammatory bowel diseases.

