What is metabolic syndrome – and do we really need to worry about it?
Metabolic syndrome is a growing health concern worldwide. So, what is metabolic syndrome? It’s a group of risk factors including high blood sugar, belly fat, and abnormal cholesterol. Metabolic syndrome symptoms are often silent but increase your risk of heart disease and diabetes. Knowing what is metabolic syndrome and spotting metabolic syndrome symptoms early is crucial. Metabolic syndrome is serious.
Introduction – A Modern Health Crisis
Metabolic syndrome is a growing global health crisis, often overlooked due to its silent nature. But what is metabolic syndrome? It refers to a group of risk factors—high blood pressure, excess abdominal fat, elevated blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels. These metabolic syndrome symptoms may not seem urgent but significantly increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Recognizing what is metabolic syndrome and addressing it early through lifestyle changes is vital. As metabolic syndrome cases rise due to poor diet and inactivity, awareness and prevention become more important than ever. Don’t ignore this silent but serious threat.
Metabolic Syndrome – A Cluster of Red Flags
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of red flags signaling serious health risks. But what is metabolic syndrome really? It’s a combination of conditions like belly fat, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol. Common metabolic syndrome causes include poor diet, lack of exercise, and insulin resistance. Ignoring metabolic syndrome symptoms can lead to diabetes or heart disease. Thankfully, metabolic syndrome treatment focuses on lifestyle changes—healthy eating, regular activity, and weight management. Understanding metabolic syndrome causes and early intervention through proper metabolic syndrome treatment can prevent long-term damage. Know the signs, act early, and take control of metabolic syndrome today.
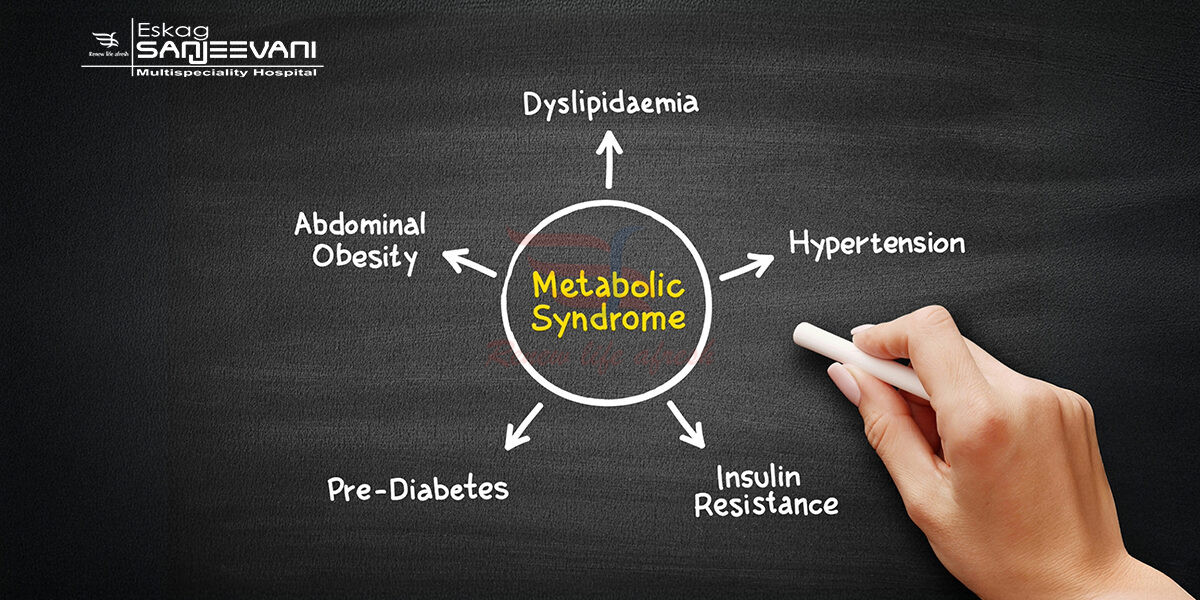
- Metabolic syndrome is defined as a group of five health risk conditions: high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess belly fat, low HDL (good cholesterol), and high triglycerides. Together, they raise the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Recognizing metabolic syndrome symptoms early is key to starting effective metabolic syndrome treatment and prevention. List and briefly explain each component:
Abdominal obesity is a major indicator of metabolic syndrome and one of its key metabolic syndromes causes. It refers to excess fat around the waist, often resulting from poor lifestyle habits. This hidden fat increases the risk of diabetes and heart disease. Addressing abdominal obesity through proper metabolic syndrome treatment is essential to reduce serious health risks. High blood pressure
High fasting glucose is a key component of metabolic syndrome and signals impaired blood sugar control. It’s one of the early metabolic syndrome symptoms and a major metabolic syndrome cause, often linked to insulin resistance. If not managed, it can lead to type 2 diabetes. Controlling blood sugar is vital in effective metabolic syndrome treatment. Elevated triglycerides
- Low HDL (good) cholesterol is a common metabolic symptom and one of the core indicators of metabolic syndrome. HDL helps remove bad cholesterol, and low levels increase heart disease risk. It’s often caused by poor lifestyle habits and is among the key metabolic syndrome causes. Improving HDL through healthy diets for metabolic syndrome is essential in effective metabolic syndrome treatment.
- To diagnose metabolic syndrome, a person must have at least three out of five specific risk factors: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high fasting glucose, high triglycerides, and low HDL (good) cholesterol. Recognizing these metabolic syndrome symptoms early is crucial. Early diagnosis allows timely metabolic syndrome treatment through lifestyle changes and targeted diets for metabolic syndrome.
This cluster is dangerous even if metabolic syndrome symptoms aren’t obvious because damage happens silently. You may feel healthy, but underlying issues like high blood sugar or low HDL quietly increase your risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Without visible signs, metabolic syndrome causes often go unchecked. Early diagnosis and metabolic syndrome treatment, including proper diets for metabolic syndrome, are essential.
What Causes Metabolic Syndrome?
Several lifestyle and health factors contribute to metabolic syndrome. These metabolic syndrome causes often work together, increasing your risk silently:
1. Poor Diet and Unhealthy Eating Habits
- High intake of processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats
- Low consumption of fiber, fruits, and vegetables
- Not following recommended diets for metabolic syndrome
2. Physical Inactivity
- Lack of regular exercise leads to weight gain and insulin resistance
- Sedentary lifestyle slows metabolism and worsens metabolic symptoms
3. Obesity, Especially Abdominal Fat
- Abdominal obesity is a key marker of metabolic syndrome
- Visceral fat disrupts hormonal and metabolic balance
4. Insulin Resistance
- Cells stop responding to insulin, causing high blood sugar
- Leads to high fasting glucose, one of the main metabolic syndrome symptoms
5. Chronic Stress and Poor Sleep
- Hormonal imbalances increase cravings, fat storage, and blood pressure
- Lack of rest slows recovery and worsens metabolic health
6. Age, Genetics & Hormonal Disorders
- Risk increases after age 40
- Conditions like PCOS and thyroid hormone disturbances contribute
- Family history also plays a role
Important: Understanding these metabolic syndrome causes helps in early prevention. Start by adopting balanced diets for metabolic syndrome, staying active, and managing stress for effective metabolic syndrome treatment.
Who is at Risk?
Anyone can develop metabolic syndrome, but certain groups face a much higher risk due to genetics, lifestyle, or existing health conditions. Identifying at-risk individuals helps with early prevention and timely metabolic syndrome treatment.
1. People with Abdominal Obesity
- Excess belly fat is a core sign of metabolic syndrome symptoms
- Visceral fat increases insulin resistance and inflammation
2. Family History of Diabetes or Heart Disease
- Genetics play a role in developing metabolic syndrome causes
- A strong family history increases overall risk
3. Adults Over Age 40
- Risk rises with age due to slower metabolism and hormonal changes
- Particularly high in post-menopausal women and aging men
4. Sedentary Lifestyle and Poor Diet
- Lack of exercise and unhealthy eating habits contribute the most to metabolic syndrome causes
- Ignoring diets for metabolic syndrome can worsen the risk
5. People with Hormonal or Metabolic Disorders
- PCOS, thyroid problems, and insulin resistance are strong triggers
- These conditions often go hand-in-hand with metabolic syndrome symptoms
Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
Metabolic syndrome symptoms are often silent or overlooked, but early warning signs can help you act before serious complications arise. Identifying these symptoms is the first step toward timely metabolic syndrome treatment.
Common Metabolic Syndrome Symptoms:
- Increased waist size
Cantal or Abdominal obesity is one of the key metabolic syndromes causes and a visible early sign. - High blood pressure
May not cause noticeable symptoms but can lead to headaches, dizziness, or chest discomfort. - Elevated fasting blood sugar
Can cause fatigue, increased thirst, frequent urination, or blurred vision. - High triglycerides & low HDL (good cholesterol)
Usually symptomless but silently increase heart disease risk. - Skin changes
Darkened patches around the neck or armpits (acanthosis nigricans) can indicate insulin resistance.
Other Warning Signs:
- Constant tiredness or low energy
- Trouble focusing or brain fog
- Unexplained weight gain, especially around the belly
Important: Even without obvious signs, metabolic syndrome can cause long-term damage. If you notice any of these metabolic symptoms, consult a doctor and start a diet for metabolic syndrome plan as part of your personalized metabolic syndrome treatment.
How Is It Diagnosed?
Diagnosing metabolic syndrome involves checking for a combination of measurable health risk factors. To be diagnosed with metabolic syndrome, a person must have at least three out of five specific conditions.
Diagnosis Criteria for Metabolic Syndrome:
Abdominal obesity
Waist circumference over 40 inches (men) or 35 inches (women)
High fasting glucose
Fasting blood sugar ≥ 100 mg/dL
High blood pressure
130/85 mmHg or higher
Low HDL cholesterol (good cholesterol)
Less than 40 mg/dL (men) or 50 mg/dL (women)
High triglycerides
150 mg/dL or higher
Key Tests to Confirm Metabolic Syndrome:
- Fasting blood glucose test
- Lipid profile (HDL and triglycerides)
- Blood pressure measurement
- Waist circumference check
Why Diagnosis Matters
Early detection of metabolic syndrome symptoms allows for prompt metabolic syndrome treatment and lifestyle changes. Understanding what is metabolic syndrome and identifying metabolic syndrome causes early can help prevent serious conditions like diabetes or heart disease.
Why You Should Be Concerned
Metabolic syndrome is more than just a collection of health numbers—it’s a serious warning sign. Even if you feel fine, this condition silently increases your risk of life-threatening diseases like heart attacks, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The danger lies in the fact that metabolic syndrome symptoms are often mild or invisible, allowing damage to build up over time. Many people remain unaware they even have it until a major health event occurs. That’s why understanding what is metabolic syndrome, recognizing early signs, and knowing the main metabolic syndrome causes—such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, and abdominal obesity—is critical. Left unchecked, it not only harms your body but can lead to long-term emotional stress and financial strain due to ongoing treatments and medications. Fortunately, with the right metabolic syndrome treatment, including targeted lifestyle changes and balanced diets for metabolic syndrome, the condition can often be reversed or effectively managed. Being informed, proactive, and making healthier choices now can prevent serious health issues later.
Prevention and Lifestyle Management
Metabolic syndrome can often be prevented or reversed through healthy lifestyle changes. The best metabolic syndrome treatment includes regular exercise, weight control, and balanced diets for metabolic syndrome rich in fiber and low in sugar. Managing stress, improving sleep, and quitting smoking are also essential. Understanding what is metabolic syndrome and addressing the root metabolic syndrome causes helps protect long-term health.
Healthy Diet Plan
A healthy diet is crucial for effective metabolic syndrome treatment. Diets for metabolic syndrome should focus on whole grains, lean proteins, vegetables, fruits, and healthy fats. Reducing processed foods, sugar, and salt helps control key metabolic syndrome symptoms. Since poor eating habits are major metabolic syndrome causes, adopting a balanced diet can prevent complications and improve overall metabolic health.
Exercise and Movement
Regular exercise plays a vital role in metabolic syndrome treatment. Physical inactivity is one of the key metabolic syndromes causes, contributing to obesity, high blood pressure, and insulin resistance. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate activity per week—like walking, cycling, or strength training—helps manage weight and reduce metabolic syndrome symptoms. Combined with proper diets for metabolic syndrome, movement is essential for long-term health.
Stress and Sleep Management
Chronic stress and poor sleep are often overlooked metabolic syndrome causes. They can worsen insulin resistance, increase blood pressure, and trigger unhealthy eating—contributing to key metabolic syndrome symptoms. Effective metabolic syndrome treatment should include stress reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing. Quality sleep (7–9 hours) supports metabolic balance. Along with diets for metabolic syndrome, managing stress and sleep is essential for recovery.
Medication and Medical Support
While lifestyle changes are the foundation of metabolic syndrome treatment, some individuals may require medication to manage specific metabolic syndrome symptoms like high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, or abnormal cholesterol levels. Medical support helps control the underlying metabolic syndrome causes when diet and exercise aren’t enough. Alongside proper diets for metabolic syndrome, regular checkups and prescribed medications can prevent serious complications and support long-term health.
Myths About Metabolic Syndrome
Many believe metabolic syndrome only affects the obese, but that’s a myth. Even people with normal weight can develop metabolic syndrome symptoms due to poor lifestyle choices. Misunderstanding what is metabolic syndrome delays early action. Some think it’s only age-related, ignoring real metabolic syndrome causes like poor diet, inactivity, and stress. Skipping proper metabolic syndrome treatment increases long-term risk. Others assume medication alone is enough, overlooking the role of tailored diets for metabolic syndrome. In reality, reversing metabolic syndrome requires both medical support and lifestyle change. Knowing the truth about metabolic syndrome causes leads to better outcomes through focused metabolic syndrome treatment and personalized diets for metabolic syndrome.
Conclusion
Understanding what is metabolic syndrome is the first step toward protecting your long-term health. Although metabolic syndrome symptoms may be silent, the risks are real. Ignoring the early metabolic syndrome causes can lead to serious complications like heart disease and diabetes. The good news? With the right metabolic syndrome treatment and lifestyle changes—including balanced diets for metabolic syndrome, regular exercise, and stress management—you can take control. Don’t wait for a diagnosis. Act now, stay informed, and prevent metabolic syndrome before it takes a toll on your life.
References
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of five risk factors like belly fat, high blood pressure, and blood sugar that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
Common metabolic syndrome causes include obesity, poor diet, physical inactivity, insulin resistance, and stress. Genetics and hormonal issues may also contribute to developing this condition.
If you have three or more signs—like high blood pressure, belly fat, or high blood sugar—you may have metabolic syndrome. A doctor can confirm with blood tests.
Metabolic syndrome raises the risk of heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and liver or kidney issues. Early detection and lifestyle changes are critical to prevent complications.
Prevent metabolic syndrome by maintaining a healthy weight, eating balanced diets for metabolic syndrome, exercising regularly, reducing stress, and avoiding smoking or excess alcohol consumption.
Yes, metabolic syndrome can often be reversed through weight loss, physical activity, stress management, and proper metabolic syndrome treatment, including dietary and medical support.
Healthy diets for metabolic syndrome help control blood sugar, cholesterol, and weight. Eating whole grains, vegetables, and lean protein is key to effective metabolic syndrome treatment. Along with avoiding fast food specially Deep fried, Spicy or those with high fat content.
Aerobic workouts like walking, cycling, and strength training help reduce metabolic syndrome symptoms by improving blood pressure, insulin sensitivity, and weight control.
Yes, metabolic syndrome can run in families. However, healthy habits like diet and exercise often prevent or delay it, even in those with a genetic predisposition.
Metabolic syndrome increases blood pressure and bad cholesterol, damaging blood vessels and significantly raising your risk of heart attacks, stroke, and cardiovascular disease.
Even modest weight loss can improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood pressure, and reduce metabolic syndrome symptoms, making it a core part of treatment.
If you have belly fat, high blood pressure, or high blood sugar, consult a doctor. Early diagnosis leads to better metabolic syndrome treatment and prevention.

