Is That Wrist Lump a Ganglion Cyst?
You wake up one morning and notice a soft, round lump on your wrist or hand. It wasn’t there before. It doesn’t hurt much—but it feels strange. Naturally, your mind jumps to worrying thoughts: Is this a tumor? Is it serious?
Finding a new lump on your body can be frightening. However, in many cases, that small, squishy swelling is something called a Ganglion Cyst—a common and harmless condition.
In this blog, we’ll explain what a Ganglion Cyst is, identify the common ganglion cyst sites, describe typical Ganglion Cyst symptoms, and help you understand when ganglion cyst treatment may be needed. We’ll also guide you on when to seek expert care at Eskag Sanjeevani Hospitals.
Key Takeaways
- Ganglion cysts are benign, fluid-filled lumps commonly found on wrists and joints. They are not cancerous.
- They may not cause pain, but treatment is needed if they press on nerves or restrict joint movement.
- Eskag Sanjeevani offers safe and effective removal options, including aspiration and surgical excision.
What is a Ganglion Cyst? The Science Behind the Lump
A Ganglion Cyst is a harmless, fluid-filled lump that forms near a joint or tendon. It is filled with fluid and usually appears on the wrist or hand. In some cases, it can also form on the ankle or foot. These cysts are common and are usually harmless.
The “Balloon on a Stalk” Explanation
A ganglion cyst can be understood like a small water balloon attached to a joint by a thin stalk. The balloon part is filled with thick, jelly-like fluid that normally helps joints move smoothly. The stalk connects the cyst to the joint or tendon. When fluid collects in this small sac, it forms a visible lump near the joint.
Who Gets Them?
Ganglion cysts are common in:
- Women more than men
- People aged 20 to 40 years
- Individuals who use their wrists or hands repeatedly
They can also occur without any clear cause.
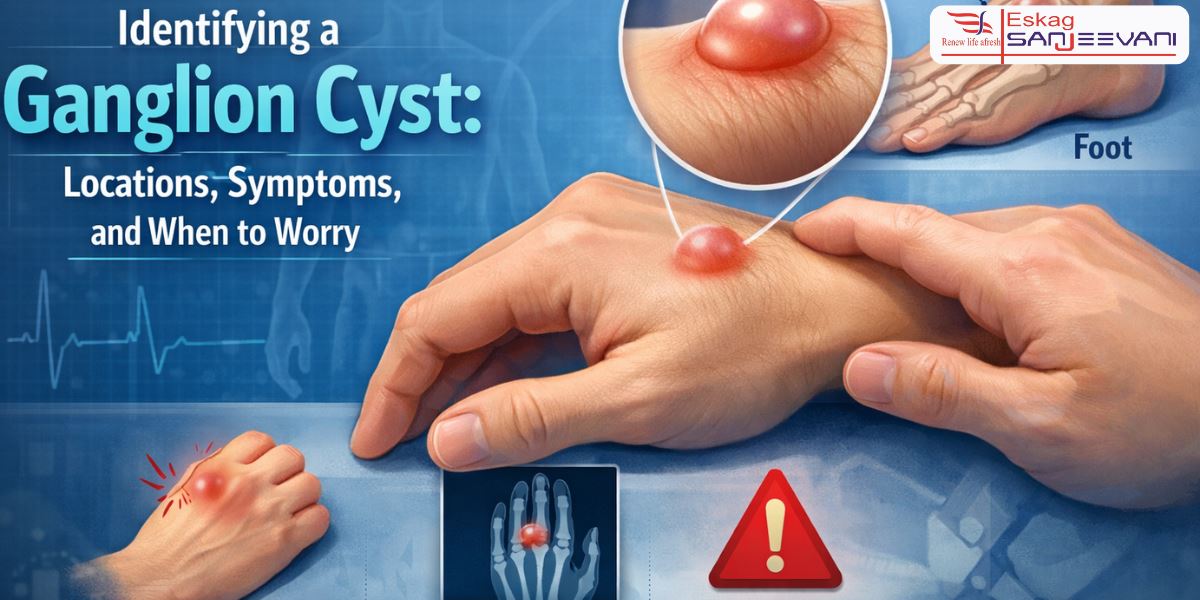
Where Do They Appear? Mapping the Locations
Understanding ganglion cyst sites helps identify the condition early. The location of ganglion cyst varies, but certain areas are more common.
1. The Wrist (Most Common Site)
The wrist is the most common place for a ganglion cyst. Most cysts appear on the back of the wrist. They look like small, round lumps and may become more noticeable when you bend your wrist. Some people may feel mild discomfort during movement.
2. The Hand and Fingers
Ganglion cysts can also form:
- At the base of fingers
- On the palm side of the wrist
- Near finger joints
These cysts may cause pain while gripping objects or bending the fingers.
3. The Feet and Ankles
Though less common, ganglion cyst sites can include the top of the foot or near the ankle joint.
These can make wearing shoes uncomfortable and may cause pain while walking.
Spotting the Signs: Ganglion Cyst Symptoms
Ganglion cyst symptoms can vary from person to person. In many cases, the cyst is painless and only noticed because of a visible lump near a joint. The swelling is usually smooth and round.
Some ganglion cysts can change in size. They may grow larger with repeated joint use and become smaller with rest. If the cyst presses on nearby nerves, it can cause pain, tingling, numbness, or weakness. The discomfort may increase when you move or strain the affected joint.
If you notice changes in size, pain, or difficulty moving the joint, it is best to consult a doctor for proper evaluation.
1. Visual Appearance
A ganglion cyst appears as a round or oval lump near a joint, most commonly on the wrist or hand. It has a smooth surface and may feel soft or slightly firm when touched. The size can vary and may change over time. The skin over the lump usually looks normal, without redness or irritation.In most cases, it does not cause pain, but the visible lump may feel uncomfortable or worrying.
2. Size Fluctuation
One unique feature of a ganglion cyst is that its size can change. It may become larger with repeated use of the joint and smaller with rest. Sometimes, the cyst may even disappear on its own and return later. This change in size happens because the fluid inside the cyst moves in and out from the joint.
3. Pain and Discomfort
The cyst itself may not hurt. However, if it presses on nearby nerves, it can cause:
- Tingling sensation
- Numbness
- Weakness in the affected area
- Pain during movement
If symptoms interfere with daily activities, medical evaluation is recommended.
Is a Ganglion Cyst Dangerous? When to Worry
Many patients ask: Is ganglion cyst dangerous?
The clear answer is No.
Ganglion cysts are benign. They are not cancerous and do not spread to other parts of the body.
However, you should consult a doctor if:
- The lump feels hard or irregular
- There is rapid growth
- It causes sudden loss of movement
- There is redness, warmth, or signs of infection
These symptoms may indicate another condition that requires further evaluation.
Treatment Options: From Waiting to Surgery
Treatment depends on the size of the cyst and your symptoms. If the cyst is painless and does not affect movement, the doctor may suggest watchful waiting. Many ganglion cysts go away on their own.
If it causes discomfort, aspiration may be done to drain the fluid with a needle. Wearing a brace can also help by limiting joint movement.
If the cyst is painful, large, or returns again and again, surgery may be advised to remove it completely and reduce the chance of it coming back.
1. Watchful Waiting
Watchful waiting means no immediate treatment is needed. If the ganglion cyst is not painful and does not affect movement, the doctor may simply monitor it. Many cysts shrink or disappear on their own over time. Regular check-ups help ensure that the cyst does not grow larger or cause problems.
2. Aspiration
Aspiration is a simple procedure used to treat a ganglion cyst. In this procedure, the doctor carefully inserts a thin needle into the cyst to drain the fluid inside. This reduces the size of the lump and relieves discomfort. The procedure is quick and usually done in the outpatient department. Sometimes, the cyst may come back after aspiration.
3. Immobilization
Immobilization means limiting movement of the affected joint. The doctor may suggest wearing a brace or splint for some time. Reducing joint movement can help decrease the flow of fluid into the cyst. This may reduce its size and ease discomfort. Immobilization is usually recommended when the cyst causes mild pain or swelling.
4. Surgery (Excision)
Surgery is recommended when the ganglion cyst causes pain, keeps coming back, or affects joint movement. In this procedure, the doctor removes the cyst along with its stalk from the joint or tendon. Removing the stalk helps reduce the chance of the cyst returning. The surgery is usually done under local or regional anesthesia. It is a safe procedure, and most patients go home the same day. After surgery, mild pain or swelling may occur, but it improves with proper care and medication.
A Strict Warning: Avoid Home Remedies
Some people try the old “Bible bump” method—hitting the cyst with a heavy object to burst it.
This is unsafe. It can cause injury, infection, and damage to surrounding tissues. Always seek medical advice instead of trying home remedies.
Why Choose Eskag Sanjeevani for Removal?
Choosing the right hospital ensures safe and effective care.
Accurate Diagnosis
Getting the correct diagnosis is important before starting treatment. The doctor will examine the lump and ask about your symptoms, such as pain or trouble moving the joint. In many cases, a physical check-up is enough to identify a ganglion cyst. If needed, the doctor may suggest tests like an ultrasound or MRI to get a clear view of the lump. These tests help confirm that it is a ganglion cyst and not another type of swelling. Proper diagnosis helps the doctor decide the best treatment and prevents unnecessary worry or wrong treatment.
Cosmetic Expertise
Since cysts often appear on visible areas like the wrist or hand, surgeons focus on minimal scarring and good cosmetic results.
Safe and Sterile Procedures
All treatments are carried out in a clean and sterile environment to ensure patient safety. Proper hygiene and infection control measures are strictly followed during both aspiration and surgery. This reduces the risk of infection and supports a smooth recovery.
Wrapping Up!
A Ganglion Cyst may look worrying, but it is usually harmless. These fluid-filled lumps often appear on the wrist, hand, or foot. They are not dangerous, but sometimes they can cause discomfort or make it hard to move the joint.
If you notice a lump that does not go away or if it causes pain, see a doctor. Early check-up helps find the exact cause and gives you peace of mind.
Do not ignore it. Book an appointment with the Orthopedic department at Eskag Sanjeevani Hospitals for proper advice and safe treatment.
Yes. Nearly half of all Ganglion Cysts disappear without treatment, although it may take time.
The procedure is done under local or regional anesthesia, so you won’t feel pain during surgery. Mild soreness afterward is manageable with medication.
The back of the wrist is the most common location, followed by the front of the wrist and the base of the fingers.
If it bursts internally, the fluid is absorbed by the body. It is not dangerous, but the area may be tender, and the cyst may return.

